AI has slipped into everyday business life. In 2026, it helps write emails, break down documents, analyse numbers, create images & animations and support the decisions companies make every day
The real question is no longer “Should we use AI?” but:
“Do we actually know what happens to the data we put into AI tools?”
Most companies don’t. And that’s where the real risk starts. This guide explains how AI tools handle your data, how to spot unsafe platforms quickly and how to choose privacy-focused AI tools that protect sensitive information without slowing your team down.
As artificial intelligence becomes embedded in daily business operations, understanding how these systems handle data is no longer optional.
Table of Contents
Why AI Privacy Is a Real Business Risk in 2026
AI adoption usually starts in small, harmless ways. Someone rewrites an email faster, pastes a report for a quick summary, drops internal notes into a prompt. At the beginning, nothing seems to go wrong.
The risk appears later, when people realise sensitive client or business data has already been shared and the obvious question comes up: where did that information go?
Many teams already use AI inside everyday workflows like content creation, scheduling, and automation, especially when experimenting with AI-powered social media marketing tools.
In 2026, this question is unavoidable. AI tools are used daily, often without oversight. Employees paste real data by default and data-protection regulations are tightening, not relaxing.
AI isn’t the issue. Using it without thinking is. That’s why privacy-focused AI tools matter not out of fear but because long-term AI use only works when data is handled safely.
How AI Tools Actually Handle Your Data (Most People Get This Wrong)
How AI Tools Actually Handle Your Data
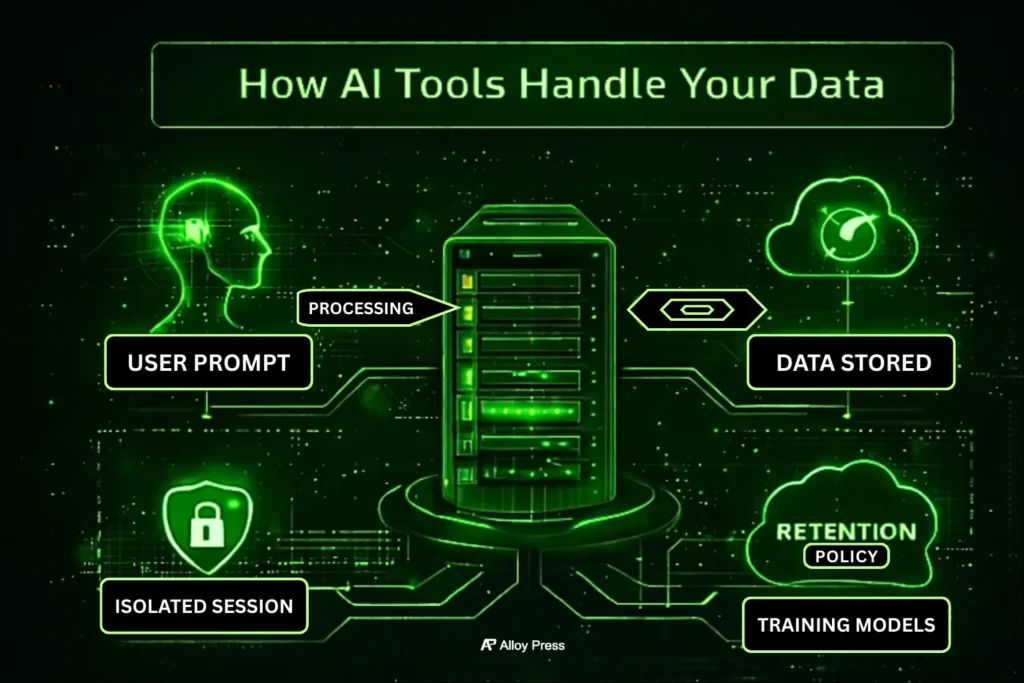
Many people assume AI tools just reply and forget everything instantly. In reality, that’s rarely how it works. When you type a prompt, several things can happen behind the scenes that most users never see or think about.
While there are thousands of AI platforms available today, not all of them are designed with privacy in mind, even among widely used popular AI tools.
Data Used for Training
Some AI tools reuse user inputs to improve their models over time. Others clearly state that customer data is not used for training at all. If this difference isn’t explained clearly and is hidden inside legal language, that tool is already a risk.
Data Retention Periods
Your prompts may be:
- Deleted instantly
- Stored temporarily
- Retained indefinitely
Retention length matters because stored data is data that can be exposed.
Prompt Storage vs Session Isolation
Privacy-focused tools keep each user session separate, so prompts aren’t mixed, stored or reused across accounts. Tools without this separation treat prompts like throwaway text, which might be fine for casual use but is risky when real business data is involved.
The Only AI Privacy Metrics That Matter

Instead of focusing only on feature lists, it makes more sense to compare AI tools based on risk and control. What really matters is how safely the tool handles data and how much control you have over what happens to it.
| What to Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Data used for training | Determines whether your inputs become part of future models |
| Data retention period | Shows how long your information exists after use |
| Encryption standards | Protects data during transfer and storage |
| Compliance support | Helps meet legal and regulatory obligations |
| Deletion controls | Ensures data can be permanently removed |
| Deployment model | Cloud, private cloud, or fully local processing |
If a tool fails even one of these checks, it doesn’t belong in serious work.
How to Spot Unsafe AI Tools in Under 5 Minutes
You don’t need technical skills to judge an AI tool. Most risks are easy to spot if you know what to check.

Check the Privacy Language
Open the privacy policy or FAQ and look at how they describe data usage. If you see vague lines like “we may use data to improve our services,” that often means your prompts could be stored or used for training. Clear tools plainly say whether your data is used or not.
Look for Prompt Privacy
Find out what happens to your conversations. Do they clearly say chats are private and not used to train models? If the answer is missing or unclear, assume your data is not fully private.
See If You Can Delete Your Data
Go to account settings or help pages and check for data deletion options. If you cannot delete your history or account data, your information may stay on their servers indefinitely.
Check for Basic Security Info
Serious platforms mention security practices like encryption or recognized standards. If there is no mention of security anywhere, that is a warning sign.
Test Their Transparency
Send a simple message to support asking if user prompts are stored or used for training. A trustworthy company will give a direct answer. A vague reply or no response is a red flag.
Be Careful With Free Tools
Free AI tools often rely on user data to improve their systems. Free is not always bad, but free plus unclear privacy rules should make you cautious.
What a Safe Tool Looks Like
A reliable AI tool explains data handling in simple language, tells you whether your data is used for training, and gives you control to delete it. If the answers are hard to find or understand, do not trust it with sensitive information.
Spending five minutes checking these points can protect you from long term privacy risks.
Security & Compliance Standards That Actually Matter
Security isn’t about fancy buzzwords. It’s about getting the basics right. At a minimum, an AI tool should encrypt data while it’s being sent and stored, limit who inside the company can access that data and keep clear logs of activity and usage.
For businesses dealing with sensitive or regulated information, compliance also matters and ignoring it is not an option.
- GDPR – protects personal data and user rights
- SOC 2 – validates security and operational controls
Tools that openly support compliance are easier to defend internally than tools that dodge the topic.
Privacy-Focused AI Tools (By Category)
These are examples only, not recommendations. The goal is to show what good privacy-focused AI tools look like, so you know what to check before choosing one.
Writing & Productivity Tools
Tools like Claude (enterprise plans) and ChatGPT Team / ChatGPT Enterprise are made for business use.
They do not use your prompts to train their models. They also keep company data separate and give admins control over usage.
These tools are useful for teams writing emails, documents and internal content without exposing private information. They are not meant for personal accounts handling sensitive business data.
This is especially important for marketing and automation work, where teams often handle client data, plans and internal numbers.
Search & Browsing
Privacy-focused search tools like Brave Search are built to reduce tracking.
They are good for research when you don’t want searches linked to user profiles or behaviour. However, they are not designed for complex business systems or large internal workflows.
Local / Self-Hosted AI
Tools such as Ollama and LM Studio run AI models directly on your own device. Your data stays on your machine and does not leave it.
This gives you full control and works well in very sensitive environments.
The extra work involved is important to understand. You are responsible for setting everything up, managing hardware, downloading and updating models, securing the system, controlling access and handling updates and fixes. If this work is ignored, the security benefit disappears.
Enterprise AI Platforms
Platforms like Azure OpenAI Service and AWS Bedrock are built for companies that need strong rules, clear control and legal compliance.
They are commonly used by regulated industries and large teams.
They cost more and take longer to set up. This is usually necessary to get clear governance, strong data separation, audit logs and formal compliance guarantees that simpler tools cannot provide.
AI Risk Assessment Checklist for Teams
Before approving any AI tool, ask one honest question: what will people actually use this for? Then review it against the following checklist to make sure real usage aligns with policy and accountability.

| Reality Check | What You Must Confirm |
|---|---|
| Actual usage | Will employees paste client, financial, or internal data into this tool? |
| Data control | Can prompts and data be deleted permanently, not just hidden? |
| Visibility | Is usage properly logged and auditable? |
| Accountability | Who is responsible if data leaks or something breaks? |
When what people actually do matches what your policy assumes, most AI mistakes never happen. Ignore this alignment and problems are guaranteed.
Best Practices for Using AI Without Data Leaks
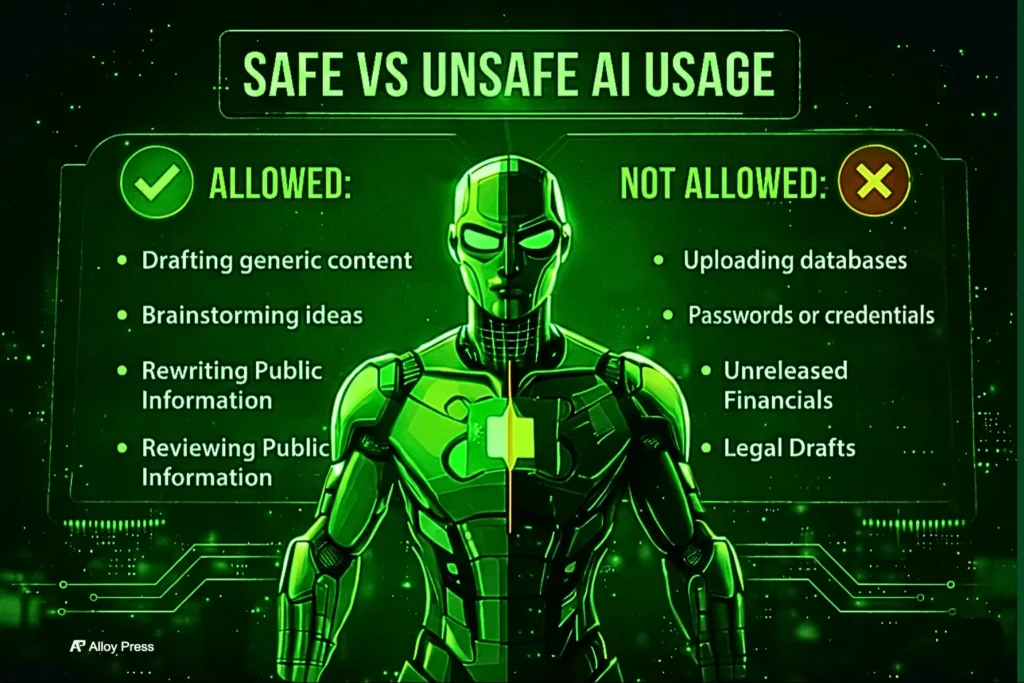
No AI tool is safe without limits. Using it for generic writing, brainstorming, or public information is fine. Feeding it customer data, passwords, unreleased numbers or legal drafts is asking for trouble.
Banning AI never works. Clear boundaries do. When people know which tools are approved and where the line is, risky side-usage disappears naturally.
Where AI Adoption Is Heading Beyond 2026
Companies that get AI right aren’t using more tools. They’re using fewer tools, with clear purpose and discipline.
Going forward, private and local AI adoption will increase, governance frameworks will get stronger and ownership of AI usage decisions will become clearer.
Privacy isn’t blocking innovation. It’s what allows innovation to grow safely without breaking trust or rules.
FAQ’s
1. If I delete my chat history, is my data actually gone from the AI’s memory?
Deleting a chat usually just hides it from your view. The company may still keep it on their servers and, if it was used to train the model, it can’t be fully removed. That’s why privacy-focused tools with zero retention are important.
2. Does using a VPN protect my privacy when I’m using AI?
A VPN can hide your location and IP address, but it does not prevent an AI from identifying you if you are logged into an account. Signing in with services like Google or Apple links your activity to you. To remain anonymous, you would need an AI that allows guest access or does not track user identities.
3. Is there an AI version of ‘Incognito Mode’?
Some AI tools in 2026, like ChatGPT and Grok, offer a “Temporary Chat” or “Privacy Mode.” When this is turned on, the AI does not keep the conversation after it’s closed and does not use it to train future models. It acts like a “burn after reading” for your digital interactions.
4. Who actually owns the data I put into a ‘Private’ AI?
Many people assume that “private” means they fully own their data or the AI’s output. In reality, AI terms of service are often unclear. Even if a tool doesn’t actively look at your data, ownership of both input and output can be uncertain.
For sensitive work, like patents or confidential scripts, check for a “Data Sovereignty” clause. This ensures you keep all intellectual property rights. And remember, with free tools, if you aren’t paying, your data is often the product.
5. Can my voice or face be ‘stolen’ if I use AI video/audio tools?
With high-quality deepfakes becoming common, many people worry about biometric harvesting. Using AI avatars or voice cloning can mean sharing your unique biometric data.
The practical advice – check if the tool offers a “Biometric Deletion” policy. By 2026, trusted tools delete your raw physical data after generating the file. If a tool reserves the right to use your likeness for model training, it could retain permanent access to your digital identity.
Final Thought
Think of AI like any powerful tool, you don’t hand it over blindly. You use it wisely. If an AI tool can’t clearly tell you how your data is protected, don’t bring it into serious work.
Pair the right privacy-focused tools with simple, clear rules, and suddenly AI stops being a hidden risk and starts giving you an edge.
In 2026, the difference between smart use and expensive mistakes comes down to one thing: clarity.









0 Comments